Mastering grammar doesn’t have to be a tedious task. This guide offers a fresh perspective on learning grammar rules, presenting engaging approaches and interactive exercises. We’ll explore various learning styles and effective strategies to keep you motivated throughout the process, ensuring that understanding grammar becomes an enjoyable journey rather than a chore.
From breaking down complex rules into manageable components to incorporating visual aids and real-world examples, this comprehensive guide equips you with the tools and techniques to grasp grammar with confidence and enthusiasm. Discover how to transform your study sessions into interactive experiences that are both educational and entertaining.
Approaches to Learning Grammar

Learning grammar effectively requires a thoughtful approach that caters to individual learning styles and preferences. A well-structured curriculum can significantly enhance understanding and retention, leading to a more confident and competent grasp of grammatical concepts. Choosing the right method and tailoring it to the learner’s needs is key to avoiding boredom and fostering a genuine love for the subject.
Diverse Approaches to Grammar Learning
Various methods exist for mastering grammar, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these approaches is crucial for selecting the most suitable technique for each learner. Traditional methods, often relying on rote memorization, contrast with more interactive and engaging strategies that emphasize practical application and real-world use. These alternative approaches often employ multimedia elements and gamification to make learning more fun and accessible.
Traditional Grammar Methods
Traditional grammar methods often focus on explicit rules and structured exercises. Students learn grammar rules through textbooks, worksheets, and memorization drills. This approach provides a clear framework and allows for a systematic understanding of grammatical structures. However, this method can sometimes be tedious and less motivating for learners who prefer more dynamic learning experiences.
Interactive and Engaging Methods
Interactive and engaging methods emphasize active participation and real-world application. These strategies often incorporate multimedia elements, gamification, and collaborative activities to enhance learner motivation and engagement. This approach allows students to connect grammar rules to practical usage, making the learning process more relevant and memorable. For example, using interactive grammar exercises or language learning apps can greatly improve student retention and comprehension.
Comparison of Approaches
| Method | Learning Style Suitability | Engagement Level | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional | Structured learners, those who thrive on clear rules and guidelines. | Potentially low, especially for visual and kinesthetic learners. | Can be tedious and demotivating for some learners; limited opportunity for practical application. |
| Interactive/Engaging | Visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners, those who prefer hands-on activities and real-world application. | High, due to active participation and varied learning activities. | Requires careful planning and design to avoid overwhelming learners; might not suit learners who prefer a more structured approach. |
Integrating Multimedia Elements
Multimedia elements can significantly enhance a grammar lesson. Videos, audio recordings, and interactive simulations can make abstract concepts more concrete and engaging. For example, a video demonstrating the use of a particular tense in a natural conversation can make the concept more relatable and easier to understand. Using animated characters or scenarios can further improve the learning experience, especially for younger learners.
Gamified Grammar Exercises
Gamified exercises, such as grammar quizzes, online games, and interactive story-building activities, can transform grammar lessons into fun and engaging experiences. Examples include grammar-based word games where players earn points for correctly identifying and using grammatical structures. Interactive storytelling apps can allow learners to create their own narratives, forcing them to apply grammar rules in context. These exercises make learning more dynamic and enjoyable, increasing student motivation and retention.
Breaking Down Complex Rules
Mastering grammar involves understanding complex rules, but dissecting them into smaller, more digestible parts is key to effective learning. This approach allows for a deeper comprehension of the underlying principles, rather than simply memorizing isolated rules. Breaking down complex rules into smaller components allows for a more focused and manageable learning process.By examining the individual elements of a rule, learners can grasp the logic and rationale behind it, fostering a more profound understanding.
This method facilitates better retention and application of grammar concepts. This section will demonstrate techniques for breaking down intricate grammatical structures, visualizing their components, and providing real-world examples to solidify understanding.
Categorizing Grammar Rules
Understanding the different types of grammar rules and their functions allows for a structured approach to learning. Classifying rules based on their function or structure creates a framework for organizing and recalling information. This structured approach is beneficial for learners of all levels, allowing them to navigate complex grammar rules with greater ease.
| Category | Description | Key Components |
|---|---|---|
| Subject-Verb Agreement | Ensuring the subject and verb in a sentence agree in number (singular or plural). | Subject, Verb, Singular, Plural |
| Tense Formation | Creating different verb forms to indicate time. | Base form, Past tense, Present participle, Past participle |
| Pronoun Usage | Using pronouns correctly to refer to nouns. | Pronoun types (personal, possessive, reflexive), Antecedent |
| Sentence Structure | Understanding the arrangement of words and clauses in a sentence. | Subject, Predicate, Clause types (independent, dependent), Phrases |
Visualizing Grammar Rules
Visual aids can significantly enhance understanding of complex grammar concepts. Diagramming sentences, using flowcharts, or creating mind maps can help learners visualize the relationships between different parts of a sentence. Utilizing these visual tools aids in a more comprehensive understanding of the structure and function of grammar rules.For example, a sentence diagram can illustrate the subject, verb, and objects in a sentence, clearly demonstrating the relationships between these components.
Illustrating Abstract Concepts with Real-World Examples
To solidify understanding, abstract grammatical concepts should be illustrated with real-world examples. Using authentic sentences from literature, news articles, or everyday conversations helps learners relate theoretical rules to practical applications. This approach makes the learning process more engaging and relevant.For example, consider the concept of subject-verb agreement. A sentence like “The cat sleeps soundly” adheres to the rule, while “The cats sleep soundly” is also grammatically correct.
Identifying Patterns and Exceptions
Grammar rules often have patterns and exceptions. Identifying these patterns allows for a more nuanced understanding of the rule’s application. Learning exceptions is crucial for avoiding common errors. Recognizing exceptions is an important aspect of mastering grammar.For example, the rule of subject-verb agreement typically follows a straightforward pattern. However, exceptions exist with collective nouns (e.g., “The team is ready”
team is singular).
Interactive Learning Activities
Engaging learners actively is crucial for effective grammar instruction. Interactive exercises transform passive learning into an active, problem-solving experience. This approach fosters deeper understanding and retention of grammatical rules. By incorporating diverse learning styles and providing constructive feedback, instructors can optimize the learning process.Interactive exercises go beyond rote memorization. They encourage learners to apply grammatical concepts in practical scenarios.
This active engagement solidifies understanding and allows learners to identify and rectify errors.
Types of Interactive Exercises
Interactive exercises should cater to various learning styles. Visual learners benefit from diagrams, charts, and illustrations that visually represent grammatical structures. Auditory learners thrive in activities involving listening, speaking, and discussions. Kinesthetic learners often find hands-on activities and simulations most effective. A well-rounded approach addresses these diverse preferences.
Visual Learning Activities
Visual aids significantly enhance understanding of grammatical concepts. Use diagrams to illustrate sentence structures, charts to depict different tenses, and illustrations to represent parts of speech. For instance, a diagram showing the subject-verb-object order in a sentence helps visual learners grasp the concept. Furthermore, flashcards with grammatical terms and examples can serve as valuable tools for memorization.
Auditory Learning Activities
Activities involving speaking and listening are ideal for auditory learners. Role-playing scenarios allow learners to practice using grammar rules in conversational settings. Listening to dialogues and identifying grammatical errors in recordings is another effective approach. Dictation exercises can help improve learners’ ability to apply grammatical rules in writing.
Kinesthetic Learning Activities
Hands-on activities provide a tangible experience for kinesthetic learners. Creating sentence diagrams, rearranging words to form grammatically correct sentences, or using manipulatives to represent grammatical elements can be effective. Games like creating and solving grammar puzzles can provide engaging kinesthetic practice.
Error Analysis and Feedback
Effective interactive exercises incorporate error analysis and feedback mechanisms. Provide specific, constructive feedback to learners, explaining the reasons behind errors and offering alternative solutions. This personalized feedback facilitates self-correction and prevents repetition of mistakes. For example, instead of simply marking an answer as incorrect, explain the grammatical rule that was violated.
Incorporating Different Learning Styles
An effective approach should incorporate diverse learning styles. A comprehensive set of interactive exercises should include activities designed for visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners. For example, a visual learner might benefit from a grammar diagram exercise, while an auditory learner might find a sentence-building activity more engaging. Kinesthetic learners might excel in a grammar game where they physically rearrange words.
Resources for Interactive Activities
Numerous resources can be used to develop interactive grammar activities. Online platforms, such as Quizizz, Kahoot!, and Blooket, offer pre-made interactive exercises. Educational websites and apps provide templates for creating personalized quizzes and activities. Furthermore, educational books and journals often contain examples of interactive activities. Additionally, collaborating with other educators to share resources and ideas is invaluable.
Motivation and Engagement

Maintaining student motivation is crucial for effective grammar learning. A positive and supportive learning environment, coupled with realistic goals and consistent feedback, significantly impacts the student’s engagement and long-term success. Celebrating milestones and tailoring activities to individual preferences further enhance the learning experience, fostering a love for grammar rather than viewing it as a tedious task.Effective grammar learning hinges on more than just understanding rules.
Students need to be actively engaged and motivated to retain and apply the knowledge. This requires creating a learning environment that encourages participation, celebrates progress, and fosters a genuine interest in the subject matter. A motivated student is a more successful student.
Strategies for Maintaining Motivation
Consistent motivation is a key factor in successful grammar learning. Students who feel engaged and supported are more likely to stay on track and achieve their learning goals. Implementing a variety of learning methods can keep the learning process dynamic and interesting. Establishing clear expectations and providing opportunities for practice are essential for sustained motivation.
- Establish Clear Learning Goals: Clearly defined learning goals, broken down into smaller, achievable objectives, help students understand the purpose of their learning and track their progress. This provides a sense of accomplishment and encourages them to continue their efforts. For example, a student might set a goal of mastering verb conjugations in French within a month, then break this into weekly targets.
- Provide Regular Feedback: Constructive feedback is crucial for improvement. Students need to understand their strengths and areas needing attention. Providing timely and specific feedback helps students understand how to improve their understanding of grammar rules and motivates them to keep learning.
- Incorporate Variety in Learning Activities: Utilizing a diverse range of learning methods, such as games, interactive exercises, and real-world applications, keeps the learning process engaging and prevents boredom. This ensures the student stays interested and committed to their learning.
Creating a Positive and Supportive Learning Environment
A supportive learning environment fosters a sense of belonging and encourages active participation. This includes encouraging questions, celebrating successes, and addressing challenges with empathy.
- Encourage Collaboration: Encouraging collaborative learning through group activities or peer tutoring allows students to learn from each other, share their perspectives, and provide support. This dynamic fosters a sense of community and strengthens learning.
- Celebrate Milestones and Achievements: Recognizing and celebrating small victories, such as correctly identifying a grammatical error or successfully completing a challenging exercise, boosts motivation and reinforces positive behavior. This reinforces the value of learning and encourages continued effort.
Importance of Setting Realistic Goals and Providing Regular Feedback
Setting achievable goals and providing consistent feedback are essential for maintaining motivation and progress. Realistic goals create a sense of accomplishment and avoid feelings of frustration.
- Setting Realistic Goals: Unrealistic expectations can lead to discouragement. Goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). A realistic goal is to understand the different sentence structures in English within a specific timeframe, rather than aiming to master every grammar rule in a short period.
- Providing Consistent Feedback: Regular feedback, both positive and constructive, helps students understand their progress and identify areas where they need to focus their efforts. It fosters a continuous learning cycle and promotes a sense of ownership in the learning process.
Methods for Celebrating Milestones and Achievements
Celebrating milestones and achievements fosters a positive learning environment. This can range from simple acknowledgments to more elaborate celebrations.
- Public Recognition: Public acknowledgment of accomplishments, such as posting student work or highlighting successful projects, can boost motivation and create a sense of pride among students. It can also encourage other students to strive for similar success.
- Rewards and Incentives: Small rewards or incentives can reinforce positive behavior and motivate students to continue learning. This could include small prizes, certificates of achievement, or even extra time for leisure activities related to grammar.
Incorporating Learner Preferences and Interests
Understanding and catering to learner preferences and interests enhances engagement and fosters a more personalized learning experience. This can include adapting learning materials to suit individual styles or incorporating topics that pique students’ curiosity.
- Tailoring Activities to Preferences: Recognizing individual learning styles (visual, auditory, kinesthetic) and adapting learning activities accordingly can enhance comprehension and engagement. For instance, visual learners might benefit from diagrams and charts, while kinesthetic learners might thrive in hands-on activities.
- Connecting Grammar to Real-World Applications: Connecting grammar rules to real-world scenarios and examples can make learning more relevant and engaging for students. This could involve analyzing articles from newspapers, analyzing song lyrics, or writing creative stories.
Practical Application and Real-World Examples

Mastering grammar rules isn’t just about memorizing intricate structures; it’s about applying them effectively in various communication scenarios. This section delves into the practical application of grammar in everyday speech and writing, highlighting its role in different contexts and genres. By understanding how grammar functions in real-world situations, learners can enhance their communication skills and ensure clarity and impact.Applying grammar rules correctly is crucial for effective communication.
Clear and concise language, achieved through proper grammar, ensures that your message is understood precisely, avoiding ambiguity and misinterpretations. Whether you’re crafting a formal business email or engaging in a casual conversation, correct grammar builds credibility and fosters trust.
Everyday Communication
Grammar rules govern the structure and usage of words in sentences, which directly affects how we understand each other. Using the correct tense, subject-verb agreement, and punctuation marks is essential for conveying the intended meaning. Consider the difference between “I went to the store” (past tense) and “I am going to the store” (future tense). This seemingly small difference drastically alters the message, conveying different intentions.
In everyday conversations, grammar helps us convey our thoughts and feelings with clarity.
Formal Writing
Formal writing, such as academic papers, business letters, and legal documents, requires a high degree of grammatical accuracy. Maintaining consistent sentence structure, proper use of punctuation, and adherence to established conventions are vital. In academic papers, clear and precise language ensures that arguments are presented logically and without ambiguity. In business letters, proper grammar demonstrates professionalism and respect.
Informal Conversations
Even in informal conversations, grammar plays a role, though its application may differ from formal settings. While colloquialisms and contractions are often acceptable, maintaining clarity and avoiding ambiguity is still important. The use of correct subject-verb agreement, appropriate word order, and proper tense usage enhances the understanding and impact of the message, even in casual conversations.
Creative Writing
Creative writing, such as novels, poems, and scripts, allows for greater flexibility in grammatical structure, while still needing careful consideration. Authors may choose to break grammatical conventions to create specific effects, but understanding the fundamental rules allows for deliberate choices. For instance, a poet might use unusual sentence structures or non-standard punctuation to evoke a particular mood or tone.
Genres of Writing
The application of grammar varies across different genres of writing. A formal report requires precise language and adherence to specific structures, while a fictional narrative might utilize more stylistic freedom. This table illustrates the relevance of grammar rules in various contexts:
| Genre | Context | Grammar Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Formal Reports | Academic papers, business proposals | Accuracy, precision, conciseness |
| Informal Emails | Personal correspondence | Clarity, conciseness, appropriate tone |
| Creative Fiction | Novels, short stories | Style, effect, narrative flow |
| Journalism | News articles, editorials | Accuracy, clarity, objectivity |
Resources for Practical Application
Numerous resources provide examples of correct and incorrect grammar usage, including grammar textbooks, style guides (like the Chicago Manual of Style), online grammar checkers, and language learning platforms. Websites like Grammarly offer comprehensive grammar assistance and real-world examples to enhance understanding and application. These resources provide valuable insights into the intricacies of grammar and its application in diverse situations.
Visual Aids and Diagrams

Visual aids play a crucial role in making grammar learning more engaging and effective. They transform abstract concepts into tangible representations, facilitating a deeper understanding and retention of rules. By visually presenting grammatical structures and relationships, learners can grasp complex ideas more readily and connect them to concrete examples.Visual aids, when strategically employed, can bridge the gap between theoretical explanations and practical application.
They cater to different learning styles, enhancing the overall learning experience. Furthermore, well-designed diagrams and illustrations serve as valuable tools for both instructors and students, fostering active learning and promoting a more dynamic learning environment.
The Role of Visual Aids in Grammar Learning
Visual aids, including diagrams and illustrations, significantly enhance grammar learning by providing a concrete representation of abstract grammatical concepts. They offer a visual framework for understanding complex grammatical structures, relationships, and patterns. This visual approach fosters a more intuitive grasp of the subject matter, making it easier to internalize and apply the rules in context.
Examples of Diagrams and Illustrations
Numerous types of diagrams and illustrations can effectively illustrate grammatical concepts. For example, a tree diagram can visually represent the hierarchical structure of a sentence, highlighting the relationships between different parts of speech. A flow chart can depict the steps involved in a specific grammatical process. Furthermore, a simple Venn diagram can illustrate the overlap and differences between various grammatical structures.
Creating Simple Yet Effective Diagrams
Creating effective diagrams requires a clear understanding of the grammatical concept being illustrated. Start by identifying the key elements and relationships involved. Then, select a diagram type that best visualizes these elements. Use clear and concise labels to ensure that the diagram is easily understandable. Keep the design simple and uncluttered, avoiding unnecessary details.
For complex rules, break down the concept into smaller, manageable parts, illustrating each component separately before integrating them into a larger diagram.
Incorporating Visual Aids into Learning Materials
Incorporating visual aids into learning materials is crucial for enhancing engagement and understanding. Visuals can be integrated into presentations, worksheets, and interactive exercises. Include diagrams and illustrations within the learning material to visually represent grammar concepts. Ensure that visuals are placed strategically to support and enhance the learning process, not simply to decorate. Consider using interactive tools that allow learners to manipulate diagrams and illustrations, promoting active engagement with the material.
List of Online Resources for Visual Aids and Diagrams
- Grammarly: Offers interactive tools and resources that use visuals to illustrate grammar rules.
- Merriam-Webster Dictionary: Provides examples of grammatical structures in various contexts, often with accompanying diagrams or illustrations.
- Khan Academy: Features video lessons and exercises that utilize diagrams to explain grammar concepts in a clear and engaging way.
- EnglishClub: Offers various grammar resources with visual aids, including explanations and examples.
Last Point
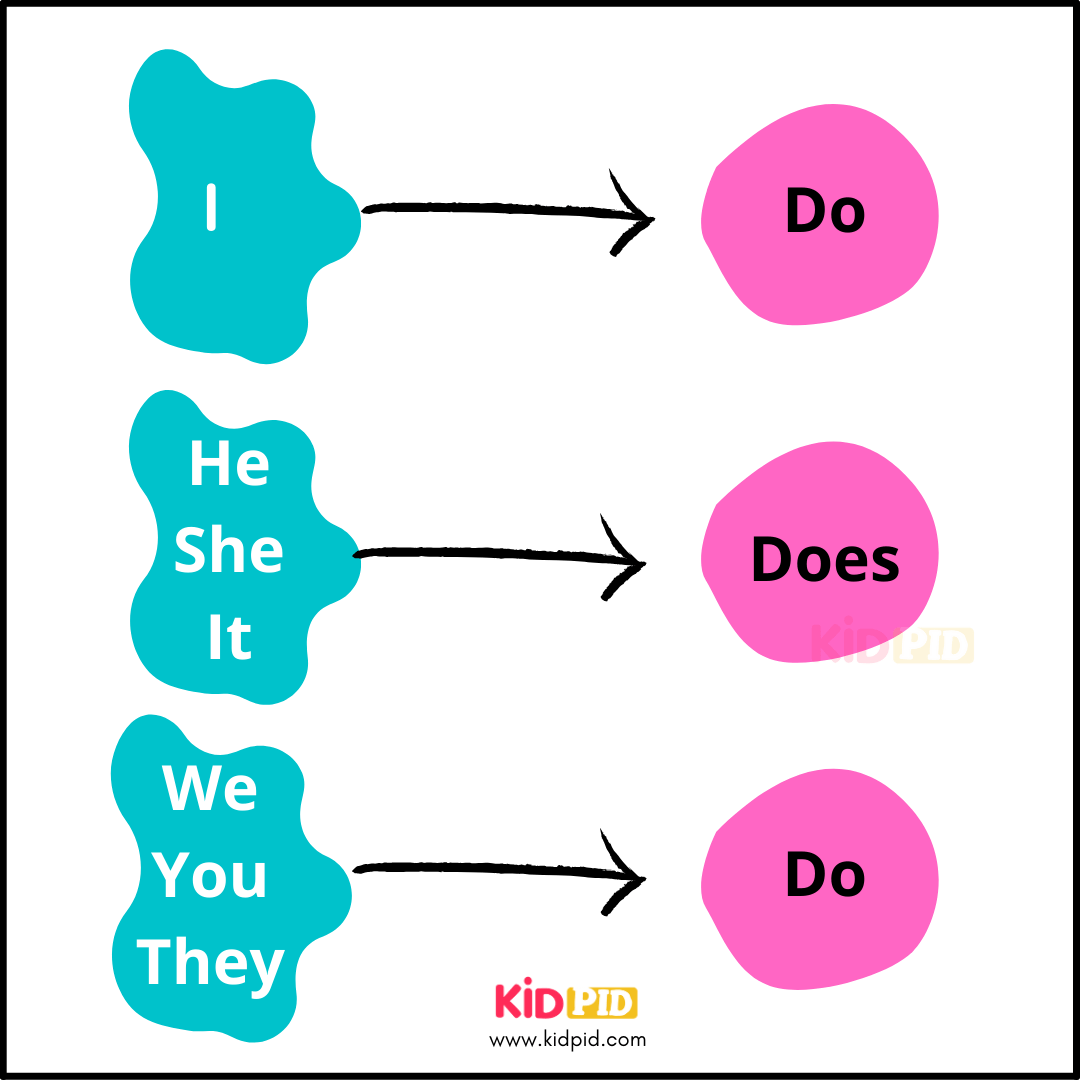
In conclusion, this guide provides a multifaceted approach to learning grammar, emphasizing engagement, motivation, and practical application. By exploring diverse learning styles, breaking down complex rules, and incorporating interactive activities, we aim to transform your understanding of grammar from a daunting task into an enjoyable experience. Ultimately, mastering grammar becomes a fulfilling journey, not a tedious one.