Harnessing the power of Google Translate for language learning is a valuable approach, but it’s crucial to use it as a supportive tool, not a replacement for dedicated language study. This guide delves into effective strategies for leveraging Google Translate’s capabilities while avoiding common pitfalls, ultimately empowering learners to achieve fluency.
This article will explore practical methods for using Google Translate effectively. It will discuss how to avoid treating translation as a shortcut, and will provide specific strategies for using the tool to enhance comprehension, vocabulary, and grammar skills. Ultimately, the goal is to understand how to integrate Google Translate seamlessly into a broader language learning strategy.
Introduction to Google Translate as a Learning Tool
Google Translate, a ubiquitous online tool, can be a valuable asset in language learning. While it shouldn’t replace dedicated study, it offers unique advantages when used strategically. This article explores how to leverage Google Translate as a learning tool, highlighting the benefits and crucial distinctions between its use as a support and a crutch. It emphasizes the importance of active engagement and critical thinking to maximize learning outcomes.Using Google Translate as a learning tool involves leveraging its translation capabilities to supplement, not substitute, traditional language learning methods.
This approach can significantly enhance vocabulary acquisition, comprehension, and cultural understanding. By actively engaging with the translated text and comparing it to the original, learners can develop a deeper understanding of language nuances and improve their overall language skills.
Potential Benefits of Using Google Translate for Language Learning
Employing Google Translate effectively can provide numerous benefits. It can accelerate vocabulary building by exposing learners to a wider range of words and phrases. Furthermore, it facilitates comprehension of written materials, allowing learners to grasp the gist of texts before delving into more in-depth study. This tool can also help learners to identify grammatical structures and patterns by comparing translations with their own understanding of the target language.
Crucial Distinction: Tool vs. Crutch
A critical distinction exists between using Google Translate as a learning tool and as a crutch. As a learning tool, it serves as a supportive aid, prompting exploration and fostering independent learning. Conversely, relying on Translate as a crutch can hinder the development of essential language skills, such as grammar, pronunciation, and fluency. Active engagement with the translated text, rather than passive reliance on the translation, is crucial for meaningful language acquisition.
Understanding the nuances of a language is far more important than simply knowing how to translate it.
Strategies for Using Google Translate as a Learning Tool
Effective use of Google Translate necessitates strategic implementation. A key strategy involves using it as a starting point for deeper investigation. For example, encountering an unfamiliar word or phrase, learners can consult Translate to grasp the general meaning. This understanding serves as a springboard for further exploration using dictionaries, language learning apps, or other resources. Another important approach is to compare multiple translations from different sources.
This practice fosters critical thinking and encourages learners to evaluate the accuracy and appropriateness of various translations. By actively engaging with the translated text, learners develop a deeper understanding of language nuances. This method will help learners identify patterns, improve comprehension, and build vocabulary.
Examples of Practical Application
To illustrate the practical application of Google Translate as a learning tool, consider the scenario of learning a new language. A learner encounters a complex sentence in a text. Using Translate to understand the basic meaning provides a foundation. The learner can then delve deeper into the grammar and vocabulary, further enriching their understanding. This process fosters a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of the target language, moving beyond simple translation to a more nuanced understanding.
Effective Strategies for Using Google Translate
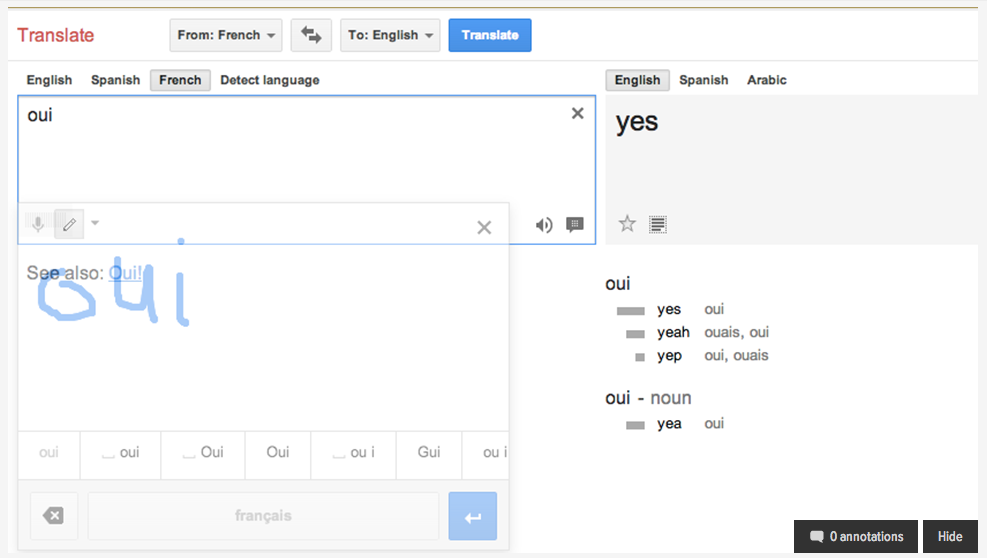
Google Translate can be a valuable tool for language learners, but its effectiveness depends heavily on how it’s used. Instead of relying solely on the translation as a substitute for learning, learners can actively engage with the tool to enhance their understanding and skill development. This section explores practical strategies for harnessing Google Translate’s capabilities to foster meaningful language acquisition.
Active Engagement with Translated Text
Passive acceptance of translated text is not an effective learning strategy. To maximize learning, learners must actively engage with the translated material. This involves comparing the translated text with the original, identifying nuances and differences, and exploring alternative translations to broaden understanding. Critically evaluating the translation is essential for developing a deeper grasp of the target language.
- Comparing Translations: Comparing Google Translate’s output with other translation resources, such as bilingual dictionaries or other online translators, can reveal potential inaccuracies or alternative expressions. This comparative analysis helps learners identify the most appropriate and natural-sounding translations.
- Exploring Context: Understanding the context of the text is crucial. Google Translate sometimes provides literal translations that don’t capture the intended meaning. Carefully examining the surrounding text and the overall situation can help learners grasp the intended message.
- Seeking Clarification: If a translation is unclear or doesn’t fully convey the meaning, learners should consult a native speaker or a reliable language learning resource for clarification. This process helps refine understanding and avoids misinterpretations.
Improving Comprehension and Vocabulary
Google Translate can be used to expand vocabulary and comprehension. By analyzing translated text, learners can identify new words, phrases, and grammatical structures. Actively incorporating these into their language learning process is essential for long-term retention and application.
- Identifying New Vocabulary: Carefully review the translated text to identify unfamiliar words and phrases. Look up their meanings in a dictionary, explore their usage in different contexts, and add them to personalized vocabulary lists.
- Understanding Sentence Structure: Analyze how the translated sentences are constructed. Note the order of words, the use of tenses, and the grammatical structures used. This analysis helps learners internalize grammatical rules and improve their ability to form correct sentences.
- Contextual Learning: Use the translated text as a springboard to learn about the subject matter and cultural context. This approach promotes a deeper understanding of the language and its cultural implications.
Utilizing Google Translate for Grammar and Sentence Structure
Google Translate can be used as a tool for learning grammatical structures and sentence patterns. However, it is crucial to critically evaluate the output, recognizing its limitations.
- Identifying Grammatical Patterns: Analyze how Google Translate translates different grammatical structures, such as verb conjugations, noun cases, or sentence types. This analysis helps learners understand the nuances of grammar in the target language.
- Comparing to Native Language Structures: Compare the translated sentence structure to the grammatical rules and patterns of the learner’s native language. This comparison helps identify differences and similarities between the languages.
- Focusing on Correct Usage: Identify areas where Google Translate struggles with accuracy or appropriate usage. Seek additional resources, such as language textbooks or online tutorials, to clarify and reinforce correct usage.
Incorporating Translated Text into Language Learning Activities
The translated text can be used in various language learning activities to reinforce understanding and promote active engagement.
- Writing Exercises: Translate short paragraphs or sentences into the target language, then retranslate them back into the original language to check for accuracy. This process helps learners practice both writing and comprehension.
- Speaking Practice: Use the translated text as a basis for conversations or role-playing activities with a language partner or tutor. This helps learners apply their knowledge in a communicative context.
- Reading Comprehension: Use the translated text as a foundation for comprehension exercises, asking learners to answer questions about the content. This activity improves understanding of the target language’s vocabulary and grammatical structures.
Example Activities
| Learning Objective | Google Translate Strategy | Example Activity |
|---|---|---|
| Improve vocabulary acquisition | Comparing translations and seeking clarification | Translate a short story from English to Spanish, then compare Google Translate’s output to a bilingual dictionary and a native speaker’s translation to identify nuanced vocabulary and expressions. |
| Enhance comprehension of sentence structure | Analyzing sentence structure and comparing to native language | Translate a paragraph from French to English, identify the grammatical structures, and compare the translation to the original to understand sentence construction. |
| Practice writing skills | Using translated text as a starting point for writing exercises | Translate a short article from German to English, then write a summary of the article in English, and compare the summary to the original article. |
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
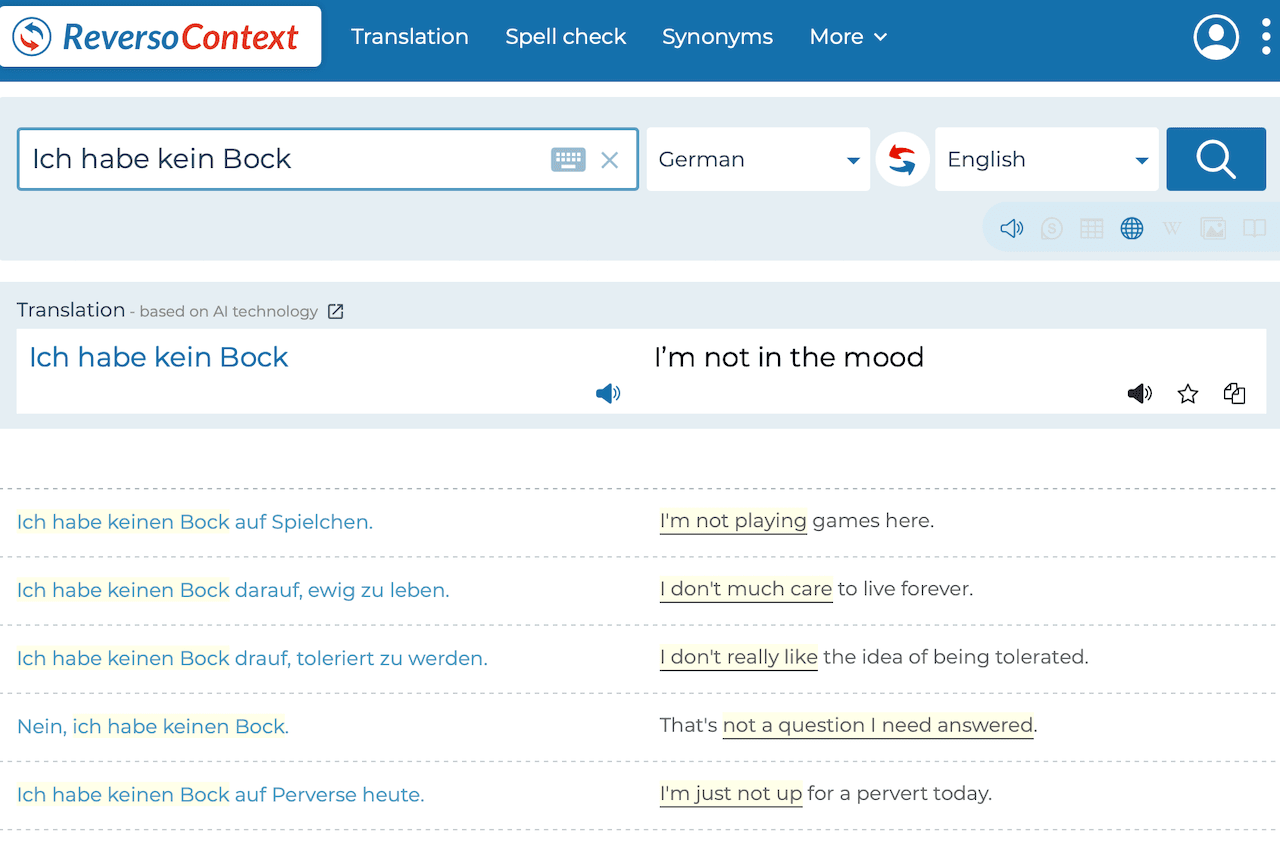
While Google Translate can be a helpful tool for initial understanding, relying on it solely for language learning can lead to significant pitfalls. This section will highlight common errors learners make and emphasize the importance of using Google Translate as a supplementary, rather than primary, learning resource. Understanding these limitations is crucial for effective language acquisition.Relying on simple translations often obscures the nuances and complexities of a language.
Direct translations frequently miss the subtle cultural contexts and idiomatic expressions that are essential for authentic communication. Over-reliance can lead to grammatical inaccuracies and a distorted understanding of the language, hindering genuine progress.
Common Translation Errors
Misinterpretations of meaning are a common consequence of using Google Translate as a primary source. The tool often struggles with figurative language, cultural references, and colloquialisms. It also frequently misinterprets tone and intent, leading to awkward or inappropriate communication. A simple phrase in one language can have multiple meanings in another, and Google Translate often fails to capture these subtle distinctions.
Lack of Contextual Understanding
Google Translate primarily focuses on literal word-for-word translations. It often fails to grasp the broader context of a sentence or paragraph. This lack of contextual understanding can lead to significant misinterpretations. For instance, a phrase used in a specific social or professional setting might be rendered inappropriately if the context isn’t considered. Understanding the social and cultural context surrounding the language is crucial for accurate interpretation.
Grammatical Inaccuracies
Google Translate often struggles with grammatical accuracy, particularly with complex sentence structures or nuanced grammar rules. It might produce grammatically incorrect sentences or misuse grammatical structures, resulting in a flawed representation of the original text. This can create a false sense of understanding, hindering the development of proper grammatical skills.
Examples of Misinterpretations
Consider the phrase “raining cats and dogs.” A direct translation might convey a literal interpretation rather than the intended meaning of heavy rain. Similarly, cultural references or idioms are often lost in translation, making the message confusing or even offensive to native speakers.
Strategies to Avoid Pitfalls
To avoid treating Google Translate as a crutch, learners should adopt a more strategic approach. A multi-faceted approach involving other learning resources and active engagement is key to effective language acquisition.
| Common Pitfalls | Strategies to Avoid Them |
|---|---|
| Over-reliance on literal translations | Supplement translations with dictionaries, native speakers, and other language learning resources. Focus on understanding the context and nuances of the language. |
| Ignoring grammatical accuracy | Combine translation with grammar exercises, native speaker feedback, and dedicated grammar study. |
| Missing cultural context | Immerse yourself in the culture through books, movies, music, and social interaction with native speakers. |
| Treating Google Translate as the sole source | Use it as a starting point for understanding, but always verify with more reliable resources. |
Integrating Google Translate with Other Learning Methods
Leveraging Google Translate effectively involves more than just translating words. Its potential extends to enhancing vocabulary acquisition, fostering cultural understanding, and refining language skills through varied learning approaches. By integrating it with other learning resources, learners can deepen their comprehension and accelerate their language learning journey.Effective strategies for combining Google Translate with other language learning resources hinge on recognizing its strengths and limitations.
It’s a valuable tool for verification and initial understanding, but not a substitute for nuanced learning experiences. Using it strategically, alongside other methods, yields the most significant benefits.
Combining with Vocabulary Acquisition
Utilizing Google Translate to verify and expand vocabulary is a valuable strategy. Start by looking up unfamiliar words in context, then check multiple translations to grasp the nuances of meaning. Compare the results with a dictionary or thesauruses to understand synonyms and antonyms. This approach can help learners grasp subtle differences in usage. For instance, using Google Translate to explore different contexts for a word, like “beautiful,” can reveal variations in meaning and usage in different cultures.
This can be complemented by flashcards, where the translated meanings are written alongside the original word, fostering active recall and comprehension.
Exploring Cultural Context
Google Translate can act as a starting point for cultural research. When encountering phrases or expressions related to cultural norms or traditions, translate them into your native language and then use search engines or cultural resources to gain a deeper understanding. For example, looking up the translation of a traditional greeting in another language and then exploring the cultural significance of that greeting can provide valuable insight.
This will allow learners to understand the underlying meaning and the cultural context behind the expression, rather than just a literal translation. This helps build cultural sensitivity and fosters more effective communication.
Comparing and Contrasting Translations
Different translation services may render the same text in various ways. This variation provides an excellent opportunity for learners to appreciate the complexities of language and understand subtle differences in meaning. Compare the translations of the same text using different translation tools to recognize how different perspectives can shape the final product. This method promotes critical thinking and encourages learners to analyze the nuances of language.
This exercise will reveal how different translations can convey various shades of meaning, making language comprehension more precise.
Integrating with Other Learning Resources
Integrating Google Translate into existing learning methods like flashcards, practice dialogues, or language exchange sessions can significantly improve the learning process. For example, when studying flashcards, include translated meanings alongside the original terms. During practice dialogues, use Google Translate to check the accuracy and fluency of your expressions. For language exchange sessions, use Google Translate as a tool for immediate translation of phrases or words.
By combining these approaches, learners can leverage the power of technology while maintaining a focus on real-world application.
Integration Methods Table
| Learning Method | Google Translate Integration | Example Activity | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flashcards | Include translated meanings alongside original terms. | Learn vocabulary for “family” in Spanish. Create flashcards with Spanish words and their English translations, and use Google Translate to confirm the accuracy of the translations. | Improved vocabulary retention and understanding of meaning in context. |
| Practice Dialogues | Use for verifying expressions and fluency. | Practice ordering food in French. Use Google Translate to check the accuracy of phrases used and to look up alternative ways of expressing the same ideas. | Enhanced fluency and ability to express oneself accurately in the target language. |
| Language Exchange | Immediate translation of phrases. | Participate in a language exchange session with a native speaker. Use Google Translate to clarify meanings or translate complex ideas. | Improved communication skills, enhanced comprehension of colloquialisms and idiomatic expressions. |
Improving Language Skills Beyond Translation
Google Translate can be a valuable tool for language learners, but it’s crucial to understand its limitations. It should not be used as a replacement for active learning and engagement with the language. Instead, it should be viewed as a supportive instrument to enhance understanding and accelerate progress. This section explores how to leverage Google Translate to augment your learning rather than simply rely on it for translations.Effective use of Google Translate extends beyond basic translation to encompass vocabulary enrichment, cultural context research, and active learning practices.
By understanding these applications, language learners can significantly improve their overall proficiency.
Vocabulary Building and Practice
Using Google Translate to expand vocabulary is an effective strategy. However, passive memorization of translated words is not enough. Active engagement with the vocabulary is key. The tool can be used to look up unfamiliar words or phrases encountered in reading materials, listening to audio, or engaging in conversations. After looking up a word, try to use it in a sentence or two in a different context to solidify your understanding.
This practice reinforces the word’s meaning and usage, moving beyond simple translation to true understanding.
Cultural Context Research
Google Translate can be a helpful tool for understanding cultural nuances. For instance, idioms, proverbs, and slang expressions often have specific cultural contexts that aren’t immediately apparent in a literal translation. By researching these elements through Google Translate and other resources, learners gain a deeper appreciation for the subtleties of the target language and culture. Understanding these nuances enhances comprehension and promotes more natural communication.
Also, researching cultural references, historical events, or social customs related to the language can provide a richer context for understanding the language.
Importance of Active Learning
Passive reliance on Google Translate can hinder the development of essential language skills. Active learning methods, such as reading authentic materials, engaging in conversations, and listening to native speakers, are crucial for improving comprehension and fluency. These methods help learners develop an intuition for the language and its intricacies, something that automated translation tools cannot replicate. By combining Google Translate with active learning strategies, learners can achieve a more profound and well-rounded understanding of the language.
Developing Comprehension Skills
Translating sentences word-for-word often misses the nuances of the target language’s structure and grammar. To improve comprehension beyond basic translation, learners should focus on understanding the underlying meaning and context of the sentences, rather than just translating individual words. This involves paying attention to sentence structure, identifying key words, and understanding the implied information. Using Google Translate to clarify specific parts of a sentence can be helpful, but it should be used as a springboard to deeper comprehension rather than the final answer.
A Table of Language Skill Enhancement Strategies
| Language Skill | Google Translate Application | Activity Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Vocabulary Acquisition | Lookup unfamiliar words and phrases. | Create flashcards with translated words and their usage examples. Use the words in sentences. |
| Cultural Understanding | Research idioms, proverbs, and slang. | Read cultural articles and watch videos about the target culture. Identify the cultural contexts of words and expressions. |
| Comprehension Enhancement | Clarify sentence structure and grammar. | Analyze sentences for meaning beyond literal translation. Practice summarizing and paraphrasing texts. |
Specific Examples and Case Studies
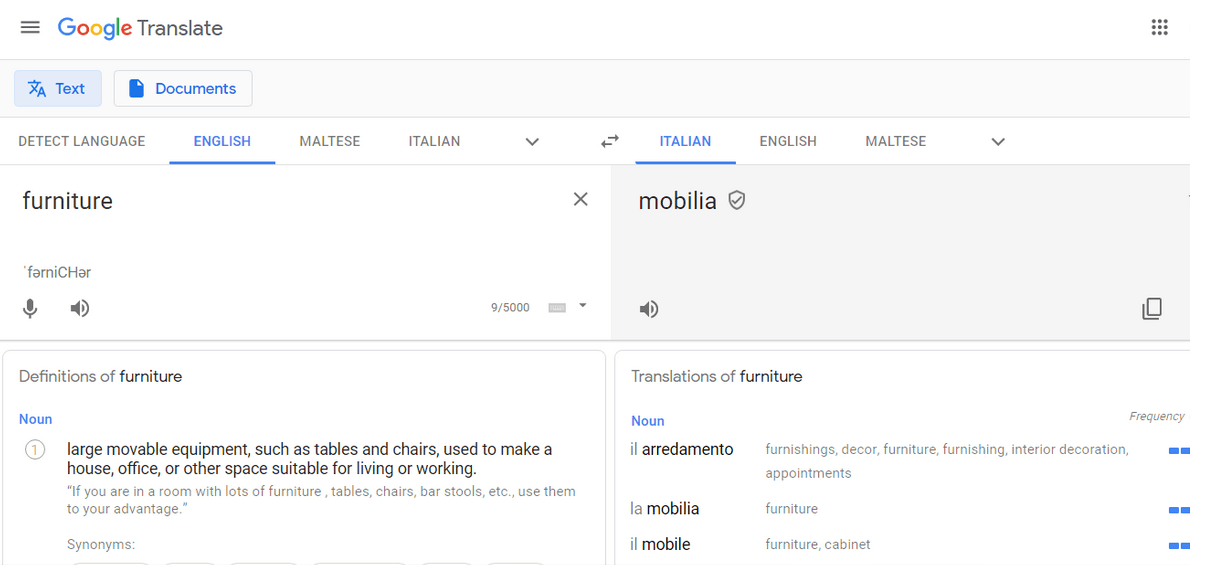
Leveraging Google Translate effectively as a learning tool requires a strategic approach, recognizing its strengths while avoiding pitfalls. This section presents real-world examples demonstrating how learners successfully used Google Translate to enhance their language skills without relying on it as their primary learning method. These case studies highlight the importance of integrating translation tools with other learning strategies for lasting comprehension and fluency.Successful learners often used Google Translate as a springboard for deeper exploration, recognizing its limitations and supplementing its output with other resources.
Successful Integration of Google Translate
Understanding how learners effectively incorporated Google Translate into their language learning journey is crucial. Successful integration involves using the tool as a stepping stone, not a replacement for dedicated study. Learners who successfully used Google Translate avoided relying on it for complete understanding, instead using it to grasp the general meaning and then verifying and expanding their knowledge.
- A student studying Spanish for a trip to Mexico used Google Translate to decipher basic phrases like “Hello,” “Thank you,” and “Excuse me.” They then immersed themselves in language learning apps, practiced with native speakers, and listened to Spanish music to expand their vocabulary and conversational skills. This approach allowed them to quickly build confidence in basic interactions while simultaneously developing a deeper understanding of the language.
- A professional wanting to expand their network in a French-speaking country utilized Google Translate to understand general business correspondence. They complemented this by studying grammar, attending language classes, and practicing their French with colleagues. This method allowed them to confidently engage in professional conversations while still relying on their knowledge base.
- A software engineer learning Japanese for a new project employed Google Translate to grasp the overall meaning of technical documents. They then diligently researched specific terms and concepts through Japanese-language dictionaries and online resources. By focusing on a detailed study of the terminology, they could build a nuanced understanding of the technical content, improving their language comprehension beyond simple translation.
Overcoming Language Barriers
Google Translate can serve as a powerful tool for overcoming initial language barriers. The key lies in recognizing its limitations and not solely relying on its output. Learners who leveraged Google Translate for comprehension, then used it as a launching point for further learning, effectively used it as a facilitator, not a crutch.
- A student struggling with understanding complex German texts used Google Translate to grasp the overall meaning of paragraphs. They then diligently consulted German dictionaries and grammar resources to verify and deepen their understanding. This allowed them to improve their language comprehension, rather than simply relying on the translation for a superficial understanding.
- A traveler visiting Italy utilized Google Translate to understand basic restaurant menus and directions. After using the translation tool, they used phrasebooks and practiced speaking Italian with locals, allowing them to progressively build confidence and a nuanced understanding of the language.
Real-World Language Skill Improvement
Real-world applications of Google Translate demonstrate its utility when used strategically. Successful integration hinges on using it to build confidence, then supplementing it with deeper learning.
- A tourist in Japan used Google Translate to ask for directions and order food at restaurants. They complemented this by purchasing Japanese phrasebooks, listening to Japanese podcasts, and practicing their pronunciation with language exchange partners. This enabled them to progressively increase their fluency beyond simple translation, fostering confidence in real-life interactions.
Conclusion (Not a)
Leveraging Google Translate effectively as a language learning tool requires a strategic approach that goes beyond simple translation. This comprehensive guide has illuminated the potential of Google Translate, not as a replacement for dedicated language learning, but as a valuable support tool. Understanding its strengths and limitations, and employing it judiciously within a broader learning strategy, can significantly enhance the language acquisition process.A well-structured approach to language learning that integrates Google Translate as a supplementary resource is crucial.
By recognizing its limitations and combining it with other learning methods, learners can avoid pitfalls and achieve greater success. This approach fosters a more holistic and dynamic understanding of the language, moving beyond mere translation to comprehension and application.
Final Thoughts on Google Translate Integration
The key to successfully integrating Google Translate into a language learning routine is a nuanced understanding of its role. It should be viewed as a tool to support, not replace, the dedicated effort required for language acquisition. Learning a language is a complex process involving not just vocabulary and grammar, but also cultural context, pronunciation, and fluency. While Google Translate can provide valuable support, it cannot fully replicate the personalized interaction and feedback crucial for achieving genuine fluency.
Key Benefits of the Approach
Implementing Google Translate as a learning aid offers several significant advantages. Firstly, it provides quick access to translations and explanations, enabling faster comprehension of unfamiliar words and phrases. Secondly, it encourages active engagement with the target language, as learners must engage with the translation process to evaluate its accuracy. Finally, it facilitates exposure to diverse language structures and vocabulary, broadening the learner’s understanding of the language’s nuances.
Importance of Supplementing Google Translate
While Google Translate is a helpful tool, it’s essential to recognize its limitations. It cannot provide context, cultural nuances, or the subtleties of idiomatic expressions. Therefore, supplementing Google Translate with other learning methods, such as language exchange partners, immersion programs, or textbooks, is paramount for achieving true fluency.
Advice for Effective Use
Learners should use Google Translate strategically, focusing on specific areas where it can be most beneficial. For example, using it to understand unfamiliar vocabulary or grammatical structures. However, learners should not rely solely on the translations provided, instead using them as a starting point for further research and analysis. Employing the tool to discover different word usages, and then looking them up in dictionaries or using other resources for clarification is a crucial aspect of effective language learning.
Crucially, learners should critically evaluate the output, ensuring they understand the context and nuances of the translation.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, Google Translate can be a powerful ally in your language learning journey, but its effectiveness hinges on strategic application. This article has shown how to leverage its features while avoiding common pitfalls, emphasizing the importance of active learning and supplementing translation with other methods. Remember, Google Translate is a tool, not a crutch, and your active participation is key to unlocking its full potential.